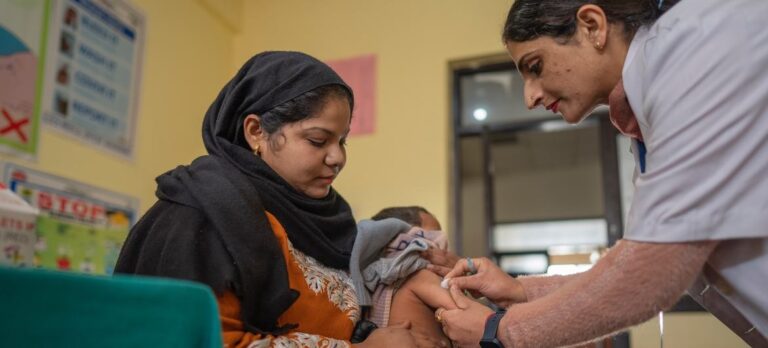
That is primarily based on The World Well being Group (WHO) and the United Nations Kids’s Fund (UNICEF) present a snapshot of vaccination developments for 14 illnesses, all of which spotlight the necessity for continued catch-up, restoration and system strengthening efforts.
“this Newest developments present many international locations are nonetheless lacking out on too many kids“, stated UNICEF Government Director Catherine Russell. “Closing the immunization hole requires a world effort, with governments, companions and native leaders investing in major well being care and neighborhood employees to make sure each youngster is vaccinated , and improve total well being care.”
Variety of kids vaccinated with three doses of diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis (DTP) vaccine – a key indicator of world immunization protection – in 2023 Stagnant at 84% (108 million).
fall again
Nonetheless, those that haven’t acquired a dose of the vaccine From 13.9 million in 2022 to 14.5 million in 2023.
The businesses report that greater than half of unvaccinated kids dwell in 31 international locations with fragile, conflict-affected and weak environments, the place kids are significantly weak to preventable infections as a result of dislocation and a scarcity of security, vitamin and well being providers. illness.
additionally, 6.5 million kids haven’t accomplished their third dose DTP vaccine is critical to attain safety in opposition to illness in infancy and early childhood.
These developments point out that international immunization protection has remained largely unchanged since 2022 and, extra worryingly, has not but returned to 2019 ranges, reflecting service disruptions, logistical challenges, vaccine hesitancy and vaccination inequalities Ready for continued challenges.
Rising measles outbreaks
Knowledge additional present that vaccination charges in opposition to the lethal measles illness have stalled, leaving practically 35 million kids with out enough safety.
In 2023, solely 83% of kids globally acquired the primary dose of measles vaccine by routine well being providers, whereas the variety of kids receiving the second dose of measles vaccine elevated barely from the earlier yr to 74%.
These figures fall in need of the 95% protection wanted to stop outbreaks, keep away from pointless sickness and loss of life, and obtain measles elimination objectives.
Prior to now 5 years, measles outbreaks have hit 103 international locations – the place about three quarters of the world’s infants dwell. Low vaccine protection (80% or much less) is a significant component. In distinction, 91 international locations with excessive measles vaccine protection had no outbreaks.
canary within the mine
“Measles epidemics are like canaries within the coal mine, exposing and exploiting immunization gaps And hit probably the most weak first,” stated WHO Director-Basic Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus.
“It is a solvable drawback. Measles vaccine is affordable and accessible even in probably the most tough locations. WHO is dedicated to working with all companions to assist international locations in closing these gaps and defending kids at excessive danger as shortly as doable.
Excellent news on international HPV vaccine protection
The brand new information additionally highlights some vibrant spots in immunization protection.
The regular rollout of plenty of new vaccines, together with these in opposition to human papillomavirus (HPV), meningitis, pneumococcal, polio and rotavirus illness, continues to develop safety, significantly beneath the Gavi-supported 57 international locations.
For instance, the proportion of adolescent women globally who’ve acquired not less than one dose of the HPV vaccine, which protects in opposition to cervical most cancers, will improve from 20% in 2022 to 27% in 2023.
“The HPV vaccine is likely one of the most impactful vaccines in Gavi’s portfolio, and Extremely, it’s reaching extra women now than ever”, stated Dr. Sania Nishtar, CEO of Gavi.
Nonetheless, HPV vaccine protection is effectively under the 90% goal to get rid of cervical most cancers as a public well being drawback, overlaying solely 56% of adolescent women in high-income international locations and solely 23% in low- and middle-income international locations.